New applications that have the potential to provide revenue streams are developing as blockchain technology advances. Smart contracts, which are self-executing programs saved on a blockchain that automatically carry out pre-defined tasks, are a promising innovation. Though this idea is still in its early stages, some businesspeople believe smart contracts may open up new avenues for people to “make money from smart contracts” in addition to more conventional approaches. This article examines the developing smart contract economy and evaluates workable tactics that one could use to perhaps benefit from this developing industry.
What Exactly Are Smart Contracts?
Simply put, smart contracts are programs stored on a blockchain like Ethereum that run exactly as coded without the possibility of censorship, downtime, or third-party interference. Using code and agreements between parties reflected in the contract’s conditions, smart contracts self-execute resulting actions like payments or asset transfers automatically under certain trigger events. Their trustless, decentralized nature enables new forms of digital agreements to take place globally 24/7 without requiring intermediaries.
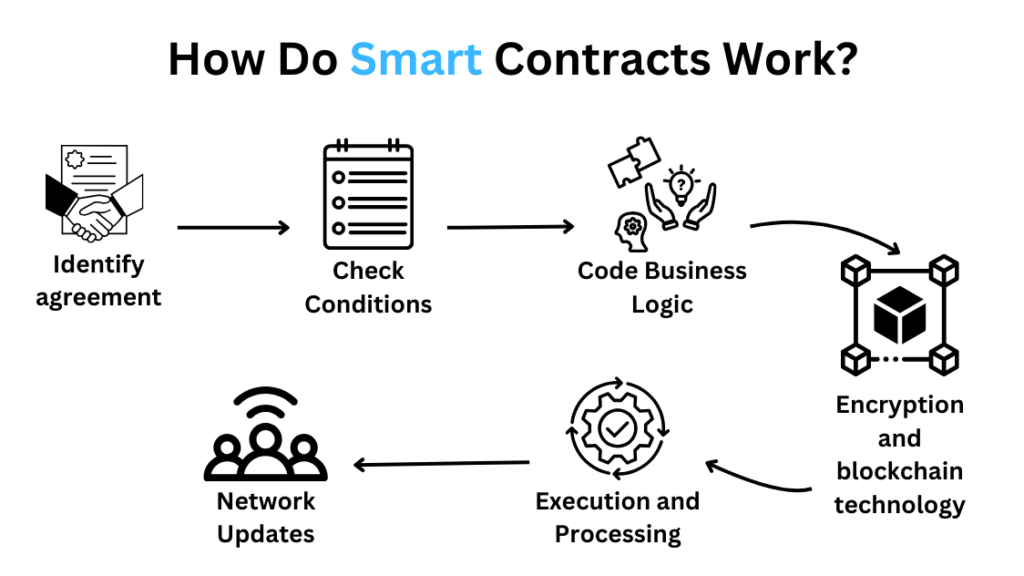
Early adopters recognized the chance to create and program unique smart contracts for customers, after which they could charge for their services. The development and upkeep of smart contracts is a chargeable profession, just like any other program or technology. Whether they are building, testing, auditing, and deploying contracts customized to customers’ application requirements, freelance programmers post hourly rates on websites. These tasks could include supply chain tracking or automating micro-investment platforms. One straightforward approach to perhaps “make money from smart contracts” is through service sales. Sustaining revenue streams are also possible with ongoing support agreements.
What Kind of Contracts Are Most Commercially Viable?
Some contract types are initially more profitable because they scale easily and meet common needs. Oracles that link triggers to real-world data perform a variety of purposes. As decentralized online markets expand, identity and reputation tracking for professional accounts may become increasingly popular. If automated investment rules for lending and investing are created securely and flexibly for future-proofing, they can also seize chances in the finance sector. Contracts for asset tokenization increase access by using fractional ownership structures. Value is ultimately driven by the trusted smart systems that address typical issues that businesses today confront.
How Can You Invest In and Profit From Smart Contracts?
Smart contract-focused crowdfunding models are starting to take shape. By supporting promising protocols in the early stage on platforms that award tokens entitling holders to share project profits, investors may be able to “make money from smart contracts”. Properly constructed decentralized autonomous organizations, or DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations), provide membership and governance over the direction of contracts by laying down foundational protocols. Additionally, people can run independently, hold token sales, and build their DAOs based on principles. Thorough investigation distinguishes promising opportunities from exaggerated notions of prudent use of funds.
As the smart contract economy flourishes, specialized roles are being defined. Qualified engineers maintaining core protocols and building applications stand to profit. Educators imparting technical skills and best security practices fill a critical function ensuring standards. Designers and product managers framing compelling end-user experiences around contract functionality optimize commercial viability and adoption rates. Compliance specialists advise maneuvering complex regulations as technology interacts with traditional systems. Community managers build valuable reputations around supported projects too through communication and advocacy.
Experienced engineers can establish consultancy practices advising organizations navigating smart contract technology. Assessing business needs, designing prototypes, overseeing deployments, arranging audits, documenting procedures, and training staff to represent services with durable demand. Consultants may charge hourly or daily rates, or structure profit-sharing agreements through DAO governance models. Leading consultancies tapping networks empower entrepreneurs to leverage contracts for new models across industries like healthcare, logistics, or gaming. Well-crafted digital identities showcase skills attracting quality clients.
What Risks Should Be Considered When Investing In Smart Contracts?
Smart contracts, like any new technology, will eventually encounter growing pains that call for careful risk management. Until it is resolved, regulatory uncertainty between jurisdictions is uncertain. Technical flaws may be found, requiring repairs or contract redesign. The factors of feasibility include committed roadmaps, team relationships, and project management. Markets and short-term excitement are unsustainable for quick-money grabbers, but significant long-term applications take time to show results. People set themselves up for long-term success by doing thorough research, investing their money wisely, and being patient.
Conclusion | Make Money From Smart Contracts
Even though they are still in the early stages of development, smart contracts offer previously unheard-of chances for creative people to design completely original models, systems, and strategies for “making money from smart contracts”. There are new roles in engineering, consulting, testing, security, and other fields. Potentially, new investable asset classes connected to digital agreements and distributed ledgers could appear. As this technology matures, those who acquire expertise early on—by building specialized tools, safeguarding networks, or resolving urgent issues—stand to gain significantly. While caution is always advised, well-thought-out methods have the potential to be profitable long-term investments that can keep up with the evolving smart contract economy.








